|
The
first and most time-consuming stage of the
project was the georeferencing and digitalisation of "analogue"
source data: topographic map in scale of 1:10000, soil-agricultural
map in scale of 1:25000 and orthorectification of scanned aerial
photographs in scale of 1:26000 (digital resolution of 2,5m). In
addition the basic (5 classes) supervised classification from aerial
orthophoto map has been made in ERDAS Imagine. 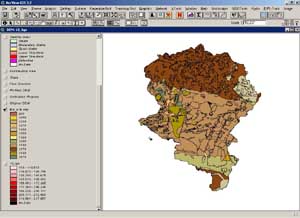
The second
stage included the creation of DEM from digitised elevation lines
(from topographic map) and points (from terrain measurements). After
initial cleaning of digitalisation errors the TOPOGRID inerpolation
method has been made in ARC/INFO programme. The initial criterion
of DEM quality was smoothness of hillshaded DEM, the quantity of
flat cells and differences between localisation of original (digitised)
and generated contours. It turned out, that TOPOGRID inerpolation
method gives good results, espetialy in the accuracy of hydrohraphy.
The later terrain measurements, made with cartographic GPS revealed
DEM errors similiar to those, assumed in TOPOGRID interpolation
options window.
|
|
|
In the
third stage we have conducted hydrological analyses:
watershed and streams (WMS 6.1), classical qualitative analyses
of surface water erosion (Jozefaciuk and Jozefaciuk, 1992): potential
water erosion (soil-slope-annual precipitation), actual water erosion
(potential water erosion-land use-agrotechnique) and gully erosion
(gully' net density). We have also made analyses of antropogenic
factor influencing the intensity and spatial diversity of surface
water erosion: the arrangement of rural ways and plots in relief
and the urgency of hardening the rural ground ways. All mentioned
analyses have been made in ArcView GIS.
|
|
|
In fourth
stage we have conducted physical modelling in EROSION 3D 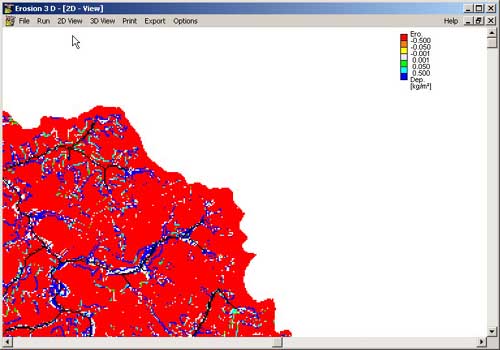 for
the purpose of quantifying the qualitative analyses results on a
"single event" basis. The basic virtues of this model
are: for
the purpose of quantifying the qualitative analyses results on a
"single event" basis. The basic virtues of this model
are:
-
relative small amount of necessary input data
-
model is basing on the physical variables, which are
easier to measure then empirical ones;
-
relatively rich theoretical and applicational literature;
-
model checked in german condition, which are relatively
similiar to polish ones
-
very good connection to GIS through ASCII grid format
|
|
|
The main goal
of fifth stage is to make full analysis of spatial diversity
of surface flow in the watershed. This analysis will be made through
spatial modelling in WMS 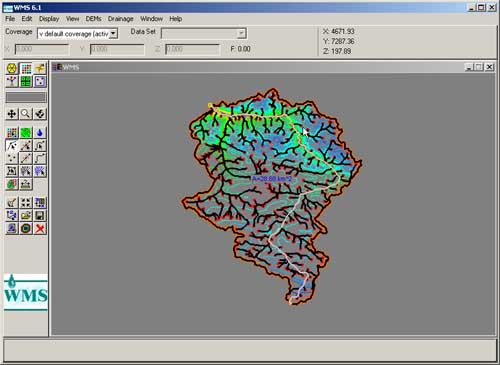 (Watershed
Modeling System). We hope to get an overview of the partipation
of particular gullies in the total inflow to Grodarz main stream
and to Kazimierz Dolny town as well as the maximum flow rates for
observed and predicted precipitation events. (Watershed
Modeling System). We hope to get an overview of the partipation
of particular gullies in the total inflow to Grodarz main stream
and to Kazimierz Dolny town as well as the maximum flow rates for
observed and predicted precipitation events.
In the last,
sixth project's stage, was the project of the erosion-control
and flood mitigating measures for the purpose of protecting valuable
landscape of Grodarz watershed and the monuments of the town Kazimierz
Dolny.Because of the specifics of Grodarz watershed area, located
interely whin the borders of Kazimierski Landscape Park, usual erosion
control meliorations can not be used and proposed meassures have
to be conservative and sustainable. The finall erosion control project
is in large extent innovative in the scale of Poland.
|
|
|

